2024. 3. 29. 19:48ㆍ카테고리 없음

1. What is rainfall
○ Rainfall is precipitation. Used in stomwater runoff calaulation(for design pipes, chanels, etc.)
simply it is rain from sky but it involved many variables
2. Water cycle
○ evaporation - condensation - precipitation
- Evaporation : Oceans, lakes, and water in soil heat up and turns into vapor and rises inot the air
- Condensation : Water vapor cools down as it rises and turns into tiny water droplets and accumulate to form clouds
- Precipitation : Water droplets combine to form bigger droplets and when Clouds get heavy enough, eventually rains fall. it run off catchment inot water bodies or soak into soil
3. Design storms
○ Hypothetical rainfall event. simulate natural event based on historical data
○ they design as how storm long and how intense that rain is
4. Anatomy of a storm
○ Pre-storm rainfall : befor it start, there can be fall pre-storm
○ Pre-burst rainfall : Period leading up to peak intensity of rainfall. make the groud satuated and it affect to calculations
○ Storm burst rainfall : maximum intensity of the storm. when design infrastucture we focus on burst phase
○ Post-burst rainfall : After the peak, decrease in rainfall intensity and eventual end
5. Storm frequency
○ it broadly grouped as
- Very frequent / Frequent / Infraquent / Rare / Extremely rare / Extreme
○ it can be measured in
- Exceedances per years(EY) / Aunnal Exceedance Probability(AEP) / Average Recurrence interval(ARI)
○ For civil design
- Common frequencies show / AEP is preffered / ARI is not used
6. Intensity Frequency and Duration(IFD)
○ Constantly upadated data of rainfall
○ AEP(=frequenct) : probability storm may occur in given year at specific location
○ intensity : rate of rainfall(mm/h)
○ Duration : length of time storm birst persist
○ Q(year) value : Design facility according to freqency)
- ~Q1 [AEP : 63.2~] : stormwater quality(WSUD)
- Q1~Q10 [AEP : 10~63.2] : Stormwater longitudinal culvert(박스) design
- Q10~Q20 [AEP : 5~10] : Roofwater design
- Q20~ Q100 [AEP : 1~5] : Floodplain mangement, waterway design, major storm even analysis
8.What is the Rational Method?
○ How much stormwater will runoff at any given location
○ Hydrological method Exstimates peak discharge from rainfall runoff
- Q = CIA/360

> Qy : Peak flow rate(m^3/s) for AEP of 1 in 'y' year
> Cy : Coefficient(계수) of runoff for AEP of 1 in 'y' year
▶if C=0.5, 50%of rainfall results in runoff exept for infilteraition
▶ City has low infilteration, so it has high Cy
> Iy : Average rainfall intensity(mm/h) for 't' hours for AEP of 1 in 'y' year
▶Intensity will increase as the storm frequency(빈도) decrease
▶Intensity will increase as the storm duration(Length of time storm's persists) decrease
> A : Catchment area
▶Determined by Countour maps, council records, Aerial imagery, Site inspection
▶we can calculate peak discharge by it's Runoff for chatchments/ inlet,pipe ststem/ road capacity ..
- Relies on the following assuption
> A storm burst of duration = time of concentration(yield the maximum of peak discharge rate)
> Entire watershed receives uniform(even) rainfall during this time of concentration
9. what is thime of concenturation[t(min)]
○ taking time from farthest point to outlet
○ relating to catchment components conditions, they make different flow path
- Roof to main system connection(t = 5m) : roof runs off roof, through downpipes(
- Kerb flow(t = 0.025L/S^0.5) : Movement over the road surface. it utilize gravity
> L : length of gutter(도로측구) flow(m) / S : Slope of gutter(%)
- Pipe flow(t = L/60V) : Movement through a pipe or conduit
> L : pipeline length (m) / V : velocity(m/s)
- Channel flow(t = L/60V): opened place to movement of water

> (V = 1/n x R^2/3 x S^1/2): velocity(m/s)
/ n : Manning's coefficient
/ R : Hydraulic radious(m)
/ s : Friction slope(m/m)
- Overland sheet flow : Overand sheet flow time
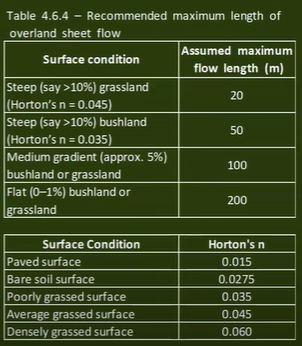
Friend's Equation(t = 107nL^0.333)(more suitable)
> n : Horton's surface toughness factor
/ L : Overland's flow path(m)
/ S : slope of serface(%)
Kinematic Wave Equation(t = 6.94(Ln)^0.6 / I^0.4S^0.3)
> n : Surface roughness coefficient
/ I : Rain fall intensity
/ L : Overland's flow path(m)
/ S : slope of serface(%)
- Concentrated overland flow(Natural Channel) ()After sheet flow reaches limit, it turns to
concentrated channel