Sight Distance at Intersections
2024. 12. 8. 10:35ㆍ카테고리 없음
- Overview : To ensure safety at intersections, drivers must be able to recognize the presence of an intersection, decelerate or stop appropriately, and identify conflicting vehicles to avoid potential collisions. Therefore, sight distance is a critical factor in the design and location of intersections. At intersections, drivers often need to observe their surroundings at angles wider than their usual field of view, which can pose challenges, especially for older drivers. For new at-grade intersections, it is ideal to design roads to meet at a 90º angle, while for redesigning existing intersections, a minimum angle of 70º should be maintained. Additionally, horizontal and vertical sight lines must be checked to ensure that natural objects or structures do not obstruct visibility, and this should be reviewed iteratively throughout the design process. These principles equally apply to pedestrian, cyclist, and railway crossings.
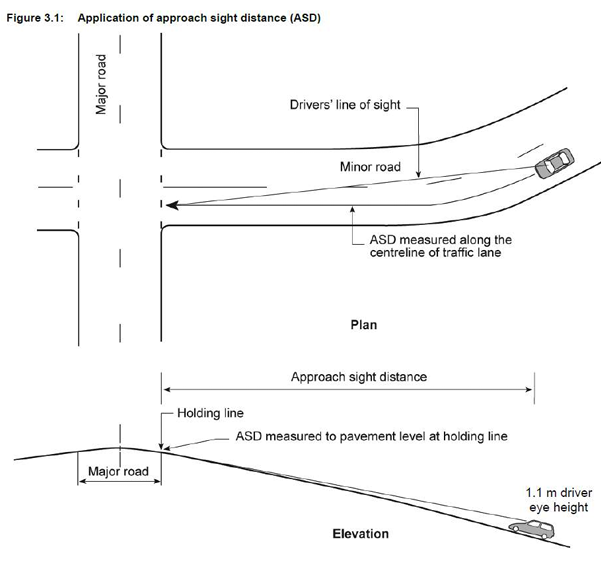
- Approach Sight Distance (ASD) : Approach Sight Distance (ASD) is the minimum sight distance required on minor road approaches to ensure drivers can recognize the presence of an intersection. It is also desirable on major road approaches to allow drivers to see pavement markings and features within the intersection, and should be provided where feasible. However, if providing ASD on the major road is impractical due to factors like cost or land impact, the minimum requirement is Stopping Sight Distance (SSD). ASD is measured from a driver’s eye height (1.1 m) to 0.0 m, ensuring visibility of line markings and kerbing at the intersection.(+ASD for trucks ensures safe stopping at the 85th percentile speed, measured from 2.4 m eye height to 0.0 m pavement level, matching SSD values in AGRD Part 3.)

- Safe Intersection Sight Distance (SISD) : is the minimum sight distance required on major roads at intersections, measured from a driver’s eye height (1.1 m) to the top of a car (1.25 m). It ensures sufficient distance for drivers to observe and react to potential conflicts, including stalled vehicles, and decelerate safely. SISD incorporates a decision time (reaction time + 3 seconds) and is measured along the carriageway to the conflict point, allowing inter-visibility between drivers on major and minor roads. It also accommodates safe crossing or turning movements for vehicles and provides adequate sight distance for articulated vehicles creating obstructions. Where possible, designers should exceed the minimum SISD values.



